Cardiometabolic
Center Alliance
Care Model

Type 2 diabetes is a serious diagnosis on its own, affecting millions in the United States and throughout the world. It is often accompanied by other serious conditions, including cardiovascular disease or diabetic kidney disease.
A Comprehensive Approach
Instead of addressing conditions or risk factors separately, the Cardiometabolic Center Alliance is taking a novel approach to treating type 2 diabetes, pre-diabetes, and related cardiovascular comorbidities together, providing team-based, comprehensive care specifically tailored to each patient.
The care model focuses on aggressively reducing risk factors—including high cholesterol, obesity, tobacco use, and lack of physical activity—and incorporating medications known to not only lower glucose levels, but proven to independently improve heart and kidney outcomes.
The Cardiometabolic Center Difference
Within this care model, a unified team cares for the whole patient.
Cardiometabolic Centers are:
- Driven by cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) focused care provider champions, such as a physician, nurse practitioner, or clinical pharmacist, in collaboration with other members of the patient’s care team.
- Supported by staff cross-trained in both cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes; including advance practice providers, clinical pharmacists, nurse navigators, diabetes care and education specialists, dietitians, and community health workers.
Patients are enrolled in an ongoing registry to track their care and outcomes over time.
Outcomes
Outcomes from the CMCA Patient Registry reveal participating sites observe substantial improvements in quality of care and better control of key cardiovascular disease risk factors, such as weight, blood pressure, lipids, and HbA1c.
Specifically, our achieved rates of optimal guideline-directed medical therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease are better than the national average.
An initial outcomes study* evaluated 606 individuals with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease and/or chronic kidney disease from six Cardiometabolic Center Alliance (CMCA) sites (age 64 years, 44% women, 78% white, median follow up 6 months).
After initiation of care at CMCA sites, large improvements in guideline-directed medical therapy and reductions in weight, HbA1c, blood pressure, total/LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and insulin requirements were observed. (p< 0.001 for all)
Our comprehensive care model has translated into improved patient reported symptoms, physical function, and quality of life.
ADA 2024: Coordinated Approach to Improve Quality of Care and Address Care Disparities in Patients with Cardiometabolic Disease
- Individuals with T2D and ASCVD that are prescribed 1) SGLT2 inhibitor and/or GLP1 receptor agonist; and 2) ACE-1 or ARB or ARNI; and 3) high-intensity statin or other high intensity lipid lowering therapy (statin plus ezetimibe, statin plus PCSK9 inhibitor, or PCSK9 inhibitor) and 4) anti-platelet or anticoagulant agent; excludes patient in whom above agents are contraindicated or not tolerated.
- Individuals with T2D and CKD that are prescribed 1) SGLT2 inhibitor and 2) ACE-1 or ARB or ARNI; excludes patients in whom above agents are contraindicated or not tolerated.
- Individuals with T2DM and ASCVD that are prescribed high-intensity statin* or statin & ezetimibe or statin & PCSK9i or PCSK9i; includes patients in whom the above agents are contraindicated or not tolerated. (* high-intensity statin therapy criteria= Atorvastatin >/= 40mg OR Rosuvastatin >/= 20mg)

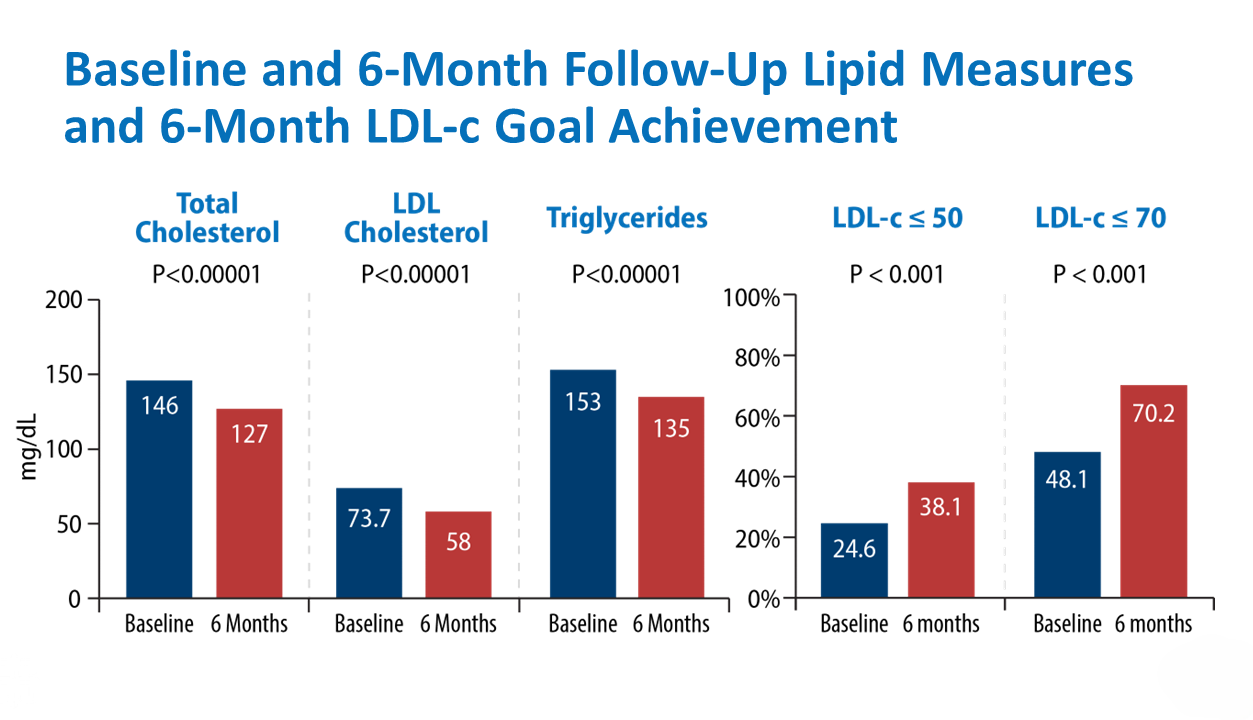
In total, 1,528 individuals with T2D and CVD and/or CKD from 6 sites were evaluated (age 66 years, 44% women, 82% white, 63% non-commercially insured median follow up 6 months).
After initiation of care at Alliance sites, large improvements were observed across multiple performance metric based on implementation of GDMT as well as those based on risk factor modification.
Quality improvements were consistent in both black and white patients suggesting that this team-based, coordinated approach utilizing standardized protocols appears to attenuate care disparities.
*For insulin-requiring individuals
Baseline Follow-Up p<0.0001 for all
Power in Numbers: Join Us
The Cardiometabolic Center Alliance is seeking to collaborate with health care organizations, academic and professional societies, and other key partners nationally and internationally in order to continue implementing this clinical model of care ensuring more patients receive comprehensive, coordinated cardiometabolic care and risk reduction.
Working collaboratively, we will lead an international initiative to significantly impact the toll of diabetes and related comorbidities. Together, we will help patients with cardiometabolic disease manage their risk factors so they can live healthier, more active lives, and help ease the burden on health care organizations caring for this complex patient population.
The Cardiometabolic Center Alliance provides its members with the training, protocols, and materials needed to establish their own cardiometabolic centers of excellence. The Alliance is committed to improving patient outcomes through improving processes and care delivery; measuring results; and expanding research opportunities on an international scale.
